EDLC Technology
 Ultracapacitor structure
Ultracapacitor structure
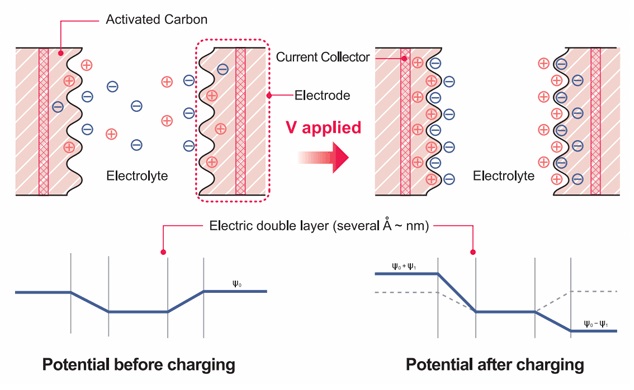
The Ultracapacitor (EDLC) consists of two electrodes immersed in the electrolyte and a separator. The objective of the latter is to prevent charge movement between two electrodes having opposite polarity.
The principle of operation of a ultracapacitor
The ultracapacitor stores energy due to electrostatic charges that are created on opposite surfaces of the electrodes belonging to the double electric layer. This layer is created between the electrolyte and the electrodes. During charging, randomly distributed electrolyte ions move toward the surface of an electrode having opposite polarity. This process has a physical, not chemical nature. In addition, it is completely reversible. In many ways, this determines the high power of ultrarcapacitors, their long life, long storage time and ease of maintenance.
A ultracapacitor is a unique energy storage device that simultaneously has high power and high energy intensity. This is what distinguishes it from traditional batteries and capacitors. The high energy intensity of supercapacitors compared to conventional electrolytic capacitors is created thanks to the electrode material. Active carbon acts in this capacity, which has two important features:- large enough surface area
- small distance between separated charges
Ultracapacitors differ from traditional batteries in their high power, long shelf life and long life, due to a special mechanism of energy storage. In conventional batteries, the accumulation and release of energy is carried out due to the chemical reaction that takes place inside the electrode material. The repeated passage of such processes inevitably leads to the degradation of this system. 
Ultracapacitors, as mentioned above, operate on the basis of the physical phenomenon of charge separation that occurs between the electrolyte ions and the charge on the electrode. A physical and easily reversible process is carried out here, so the ionistors are able to give energy much faster. In addition, they do this with more power than batteries in which a slow chemical reaction occurs. As a result, supercapacitors are ready to withstand hundreds of thousands of cycles, and this will not lead to any significant changes in their performance.
EDLC
Ultracapacitors differ in their charge-discharge characteristics from traditional batteries. For batteries, the voltage graph has a non-linear shape with a horizontal section. The graph for ultracapacitors has a constant slope. Using a special converter, the existing linear relationship with voltage is changed to constant voltage. The amount of energy stored by the capacitor is easily calculated by measuring voltage. 
Formulas for determining the energy in a capacitor
The performance characteristics of supercapacitors and batteries are determined in different measurement values - Farads and Ampere-hours. When switching to EDLC, this can confuse an unprepared user. For easy calculation of the amount of energy in the capacitor, the following formula is used:
Energy (J) = 1/2 * Power consumption (F) * Voltage squared (V).
We recommend discharge of ultracapacitors from 100% to 50% of their rated voltage. In this case, you will receive 75% of the energy stored in the drive.


